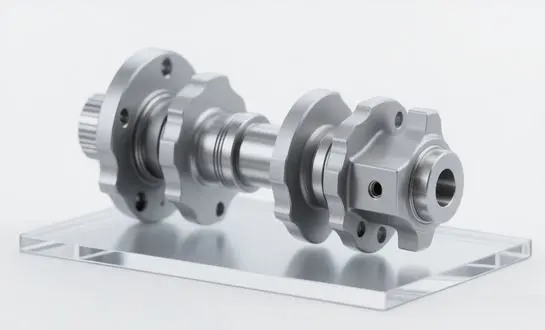
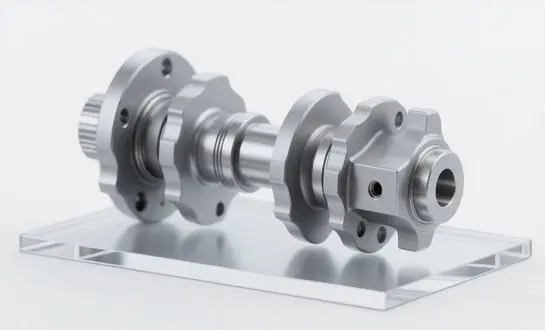
The secret to 42CrMo4's durability-boosting properties lies in its unique composition and the specialized heat treatment processes it undergoes. This combination results in a material that exhibits superior tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and toughness compared to standard carbon steel alternatives. When used in shaft forging, 42CrMo4 creates components that can endure high torque, frequent start-stop operations, and harsh environmental conditions – all while maintaining dimensional stability and operational efficiency.
What makes 42CrMo4 alloy ideal for high-stress shaft forging?
Chemical Composition and Its Impact
The 42CrMo4 alloy owes its exceptional properties to its carefully balanced chemical composition. This steel grade contains approximately 0.42% carbon, 1% chromium, and 0.2% molybdenum, along with other elements in smaller quantities. The carbon content provides strength and hardness, while chromium enhances corrosion resistance and hardenability. Molybdenum plays a crucial role in improving the steel's toughness and high-temperature strength.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
When used in shaft forging, 42CrMo4 exhibits remarkable mechanical properties. It boasts a high tensile strength, typically ranging from 900 to 1200 MPa after heat treatment. This strength, combined with excellent yield strength and good ductility, makes it ideal for components subjected to severe mechanical stress. The alloy's fatigue resistance is particularly noteworthy, allowing forged shafts to withstand cyclic loading without premature failure.
Versatility in Application
The versatility of 42CrMo4 in shaft forging extends across various industries. It's commonly used in automotive applications for crankshafts and axles, in heavy machinery for drive shafts and gears, and in the oil and gas industry for drilling equipment. This wide range of applications underscores the alloy's ability to meet diverse performance requirements and boost machine durability across different sectors.
Heat treatment processes for enhancing 42CrMo4 forged shafts
Quenching and Tempering
The quenching and tempering process is fundamental to achieving the optimal mechanical properties in 42CrMo4 forged shafts. Quenching involves heating the steel to its austenitic temperature range (typically around 850-880°C) and then rapidly cooling it in oil or water. This process creates a martensitic structure, significantly increasing the steel's hardness and strength. However, to balance this with improved toughness and ductility, tempering is performed. The tempered shaft is reheated to a lower temperature (usually between 550-650°C) and then cooled slowly, relieving internal stresses and fine-tuning the material's properties.
Normalizing
Normalizing is another crucial heat treatment process for 42CrMo4 forged shafts. This process involves heating the steel to a temperature above its critical range (typically around 880-900°C) and then allowing it to cool in still air. Normalizing helps refine the grain structure, eliminates internal stresses caused by forging, and improves the steel's machinability. This treatment is particularly beneficial for large shaft forging components, ensuring uniform properties throughout the part.
Surface Hardening Techniques
To further enhance the durability of 42CrMo4 forged shafts, various surface hardening techniques can be employed. Induction hardening is a popular choice, where the shaft's surface is rapidly heated by electromagnetic induction and then quenched. This creates a hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a tough core. Alternatively, nitriding can be used to create a extremely hard surface layer by diffusing nitrogen into the steel at elevated temperatures. These surface treatments significantly improve the shaft's resistance to wear, fatigue, and corrosion, further boosting its durability in demanding applications.
Comparing 42CrMo4 forged shafts to standard carbon steel alternatives
Strength and Durability Advantages
When comparing 42CrMo4 forged shafts to those made from standard carbon steel, the advantages in strength and durability become apparent. 42CrMo4, being a low-alloy steel, offers significantly higher tensile and yield strengths compared to most carbon steels. This translates to improved load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation under stress. Moreover, the superior fatigue resistance of 42CrMo4 means that shafts forged from this material can withstand a higher number of stress cycles before failure, greatly extending the operational life of machinery.
Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Another area where 42CrMo4 forged shafts outperform standard carbon steel alternatives is in wear and corrosion resistance. The chromium content in 42CrMo4 provides enhanced corrosion resistance, making it more suitable for applications in harsh or corrosive environments. Additionally, when properly heat-treated, 42CrMo4 shafts exhibit excellent wear resistance, maintaining their dimensional integrity and surface finish for longer periods under heavy use. This characteristic is particularly valuable in applications involving high-speed rotation or frequent contact with other components.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
While the initial cost of 42CrMo4 forged shafts may be higher than that of standard carbon steel alternatives, the long-term value proposition is compelling. The enhanced durability, longer service life, and reduced maintenance requirements of 42CrMo4 shafts often result in lower total cost of ownership over the lifecycle of the machinery. For industries where downtime is costly and reliability is crucial, the investment in 42CrMo4 shaft forging can lead to significant savings in terms of reduced replacement frequency and minimized production interruptions.
In conclusion, the use of 42CrMo4 casting in shaft forging significantly boosts machine durability through its superior mechanical properties, enhanced wear resistance, and excellent performance under high-stress conditions. By choosing 42CrMo4 over standard carbon steel alternatives, manufacturers can ensure longer-lasting, more reliable machinery across various industries. As the demand for durable and high-performance components continues to grow, 42CrMo4 remains at the forefront of materials science, offering unparalleled benefits in machine longevity and operational efficiency. For more information on how 42CrMo4 casting can improve your machinery's durability, please contact us at oiltools15@welongpost.com. Welong, your trusted partner in delivering high-quality forged components for demanding industrial applications.