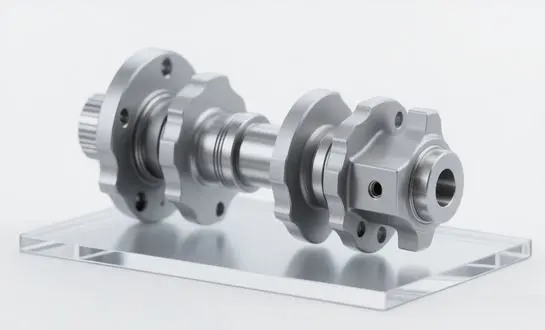
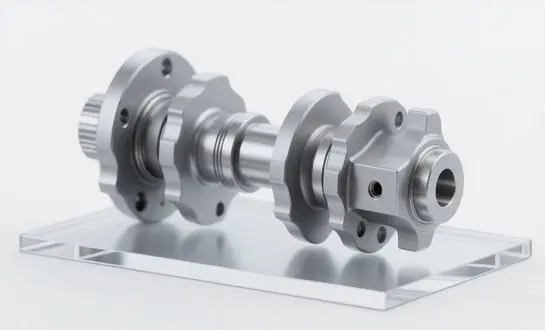
What Is a Backup Roll in Rolling Mills? How does it work?
A backup roll is a critical component in rolling mills, serving as a robust support structure for the work rolls. These massive cylinders, often made from high-quality forged steel or alloyed cast iron, are positioned behind the work rolls to provide stability and distribute the enormous pressures involved in the rolling process.
The Anatomy of a Backup Roll
The products are engineered with precision, featuring a cylindrical body, journal ends for mounting, and a carefully designed surface. Their diameter is typically larger than that of the work rolls they support, allowing them to withstand the substantial forces involved in metal forming without deformation.
Functional Mechanism of Backup Rolls
The primary function of backup rolls is to prevent deflection of the work rolls under high rolling loads. As metal passes between the work rolls, the products absorb and distribute the resulting forces, ensuring uniform pressure across the width of the material being rolled. This support mechanism is crucial for maintaining consistent thickness and flatness in the finished product.
Synergy with Work Rolls
Backup rolls work in harmony with work rolls, creating a four-high or multi-high mill configuration. This arrangement allows for greater control over the rolling process, enabling the production of thinner gauges and improved surface finishes. The interplay between backup and work rolls is a dance of precision, with each component playing a vital role in the metal forming symphony.
Backup Roll Design: How It Affects Rolling Mill Efficiency & Product Quality?
The design of the product is a critical factor in determining the overall efficiency of a rolling mill and the quality of the final product. Every aspect of the backup roll's construction, from material selection to surface finish, plays a role in its performance and longevity.
Material Selection and Its Impact
Choosing the right material for the product is paramount. High-grade steels with specific alloying elements are often used to enhance hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability. The material composition directly influences the roll's ability to withstand the cyclic stresses and high temperatures encountered during rolling operations.
Geometric Considerations in Backup Roll Design
The dimensions and profile of a backup roll are carefully calculated to optimize its performance. Factors such as roll diameter, length, and crown (slight bulge in the middle) are tailored to the specific requirements of the mill and the products being rolled. A well-designed backup roll ensures even pressure distribution and minimizes edge drop in the rolled material.
Surface Engineering for Enhanced Performance
The surface of a backup roll is engineered to balance friction, wear resistance, and heat dissipation. Various surface treatments and coatings can be applied to enhance these properties, resulting in improved roll life and better product quality. Advanced surface texturing techniques can also contribute to more efficient cooling and lubrication during the rolling process.
Optimizing Backup Roll Performance: Cooling, Lubrication & Load Distribution
Maximizing the performance of the products involves a holistic approach that addresses cooling, lubrication, and load distribution. These factors are interconnected and crucial for maintaining roll integrity and ensuring consistent product quality.
Advanced Cooling Strategies
Effective cooling is essential for prolonging the life of backup rolls and maintaining dimensional stability during rolling. Modern mills employ sophisticated cooling systems that may include internal cooling channels within the rolls, high-pressure spray nozzles, and carefully formulated coolants. These systems work in concert to manage thermal stresses and prevent roll deformation.
Lubrication Techniques for Reduced Wear
Proper lubrication is vital for minimizing friction and wear between the backup and work rolls. Advanced lubrication systems deliver precisely controlled amounts of lubricant to the roll interfaces, reducing energy consumption and extending roll life. The choice of lubricant is tailored to the specific rolling conditions and material being processed.
Intelligent Load Distribution Systems
Advanced rolling plants join advanced stack dissemination frameworks that ceaselessly screen and alter the powers connected to the Backup Rolls. These frameworks utilize sensors and actuators to keep up ideal weight over the roll confront, compensating for any misalignment or uneven wear. By guaranteeing uniform stack dissemination, these frameworks contribute to progressed item consistency and decreased roll wear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rolling process handle is a wonder of designing, with the items playing a essential part in its victory. As we've investigated, the plan, materials, and optimization of Backup Rolls are basic variables in accomplishing high-quality metal items effectively. The interaction between Backup Rolls, work rolls, and progressed control frameworks speaks to the cutting edge of metal shaping innovation. For those looking for to dig more profound into the world of rolling process components or investigate custom arrangements for their fabricating needs, we welcome you to reach out to our group of specialists. Contact us at oiltools15@welongpost.com to discover how Welong can elevate your rolling mill operations to new heights of performance and productivity.