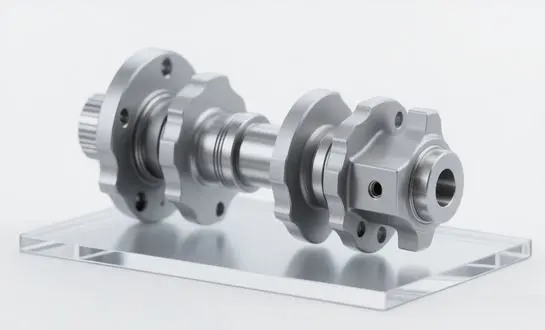
Key Components of Drilling Jars Explained
To fully grasp the functionality of drilling jars, it's essential to understand their key components and how they work together to deliver powerful impacts when needed.
Mandrel and Outer Housing
The core structure of a drilling jar consists of a mandrel that slides within an outer housing. This design allows for the necessary movement to generate impact forces.
Hydraulic Chamber
In hydraulic drilling jars, a fluid-filled chamber plays a crucial role in controlling the timing and intensity of the jar's action. The hydraulic fluid is forced through small jets, creating a delay mechanism that builds up energy before release.
Latch Mechanism
The latch mechanism is responsible for holding the jar in a cocked position until sufficient force is applied to trigger its release. This component ensures that the jar only activates when needed, preventing unintended jarring actions during normal drilling operations.
Impact Surfaces
Specially designed impact surfaces within the jar transfer the kinetic energy generated by the tool's action to the stuck point in the drill string. These surfaces are engineered to withstand repeated high-force impacts without degradation.
Drilling Jar Types: Hydraulic vs. Mechanical
Understanding the different types of drilling jars is crucial for selecting the most appropriate tool for specific drilling conditions and challenges.
Hydraulic Drilling Jars
Hydraulic drilling jars utilize a fluid metering system to control the timing of their impact. When an overpull is applied to the work string, hydraulic fluid in the jar's chamber is forced through small jets, creating a delay before the jar fires. This delay allows for the accumulation of potential energy in the stretched drill string, resulting in a more powerful impact when released.
Mechanical Drilling Jars
Mechanical jars, on the other hand, rely on a series of mechanical components such as springs and detents to create the jarring action. These jars typically have a simpler design compared to their hydraulic counterparts but may offer less control over the timing and intensity of the impact.
Choosing Between Hydraulic and Mechanical Jars
The selection between hydraulic and mechanical drilling jars depends on various factors, including:
- Well depth and temperature - Expected stuck pipe scenarios
- Desired level of control over jarring action
- Compatibility with other BHA components
Optimizing Drilling Efficiency with Jars
Proper utilization of drilling jars can significantly enhance overall drilling efficiency and reduce non-productive time.
Strategic Placement in the BHA
The positioning of drilling jars within the Bottom Hole Assembly is critical for maximizing their effectiveness. General guidelines include:
- Placing 5-6 joints of heavyweight drill pipe between the jar and accelerator
- Ensuring at least one stand of heavyweight drill pipe or drill collar above the accelerator
- Avoiding placement of larger OD tools above the jar
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance of drilling jars are essential for ensuring their reliability when needed most. This includes:
- Checking for hydraulic fluid leaks - Inspecting impact surfaces for wear
- Verifying proper functioning of the latch mechanism
- Replacing jars after recommended operating hours, especially in high-temperature environments
Integration with Advanced Drilling Technologies
As drilling technologies continue to advance, the integration of drilling jars with sophisticated measurement-while-drilling (MWD) and logging-while-drilling (LWD) tools becomes increasingly important. This integration allows for real-time monitoring of jar performance and immediate response to stuck pipe situations.
Conclusion
Drilling jars play a vital role in modern oil and gas drilling operations, providing a reliable means of freeing stuck drill strings and optimizing drilling efficiency. By understanding the mechanics, types, and optimal usage of drilling jars, operators can significantly reduce downtime and improve overall drilling performance. As we continue to push the boundaries of drilling technology, the importance of these tools in tackling challenging downhole conditions remains paramount.
For more information about drilling jars and other oilfield products, please contact us at oiltools15@welongpost.com. Welong is committed to providing high-quality drilling tools and expertise to optimize your drilling operations.
FAQ
1. How often should drilling jars be replaced?
It's generally recommended to replace drilling jars after 350 hours of operation in standard temperature conditions. However, in high-temperature environments (above 150 degrees), this limit is reduced to 200 hours to ensure optimal performance and safety.
2. Can drilling jars be used in all types of wells?
While drilling jars are versatile tools, their effectiveness can vary depending on well conditions. They are commonly used in both vertical and deviated wells, but the specific type and configuration may need to be adjusted based on factors such as well depth, temperature, and expected stuck pipe scenarios.
3. What's the difference between drilling jars and fishing jars?
Drilling jars are designed for use during active drilling operations and typically have a shorter stroke length. Fishing jars, on the other hand, are specialized tools used in recovery operations to free stuck equipment and have a longer stroke length to generate more powerful impacts.